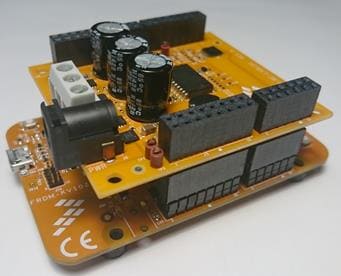
Getting Started with Freedom Development Platform for Low-Voltage, 3-Phase BLDC Motor Control
本文档内容
-
Plug It In
-
Get Software
-
Build, Run
1. Plug It In
Let's take your FRDM-MC-LVBLDC for a test drive! You have the choice of watching the sequence in a short video or following the detailed actions list below.
For those instructions, we will consider the FRDM-KV10Z board as the Freedom microcontroller board, but there are other compatible options like the FRDM-KV31F. Check the FRDM-MC-LVBLDC product page for more information about compatible Freedom microcontroller boards.
1.2 Connect the 3-Phase Motor
Plug the 3-Phase wires of the FRDM-MC-LVMTR motor, or your own motor that meets the driver specification, to the screw connector.
1.3 Attach the USB Cable
Take the micro-B USB cable included in the FRDM-KV10Z package and plug one end into your computer USB port, and the end into the micro-B port labeled "SDA USB".
This USB port provides power to the FRDM-KV10Z board, and via the onboard OpenSDA circuit, it also provides debugging, drag-and-drop flashing, and virtual serial port capabilities.
2. Get Software
2.1 Download the BLDC Motor Control Package
Download the 3-phase Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor Control package.
2.2 Program the Microcontroller Board
IAR Embedded Workbench for Arm (EWARM) version 7.40.2 or later is the development toolchain used to deploy software applications using the NXP® Connectivity stacks. NXP provides example EWARM workspace projects for you to start your development.
Follow the Getting Started instruction for your Freedom microcontroller, to download the required driver and the available IDE toolchain for your board. Then, open the corresponding project for your Freedom microcontroller board and IDE toolchain, build it and debug it.
Running a demo using Kinetis Design Studio IDE
Install KDS Updates
Before using KDS IDE with KSDK, it is recommended that you make sure that your tools are up-to-date. The steps discussed below are shown using the Windows version of KDS, but are identical for Mac and Linux users.
- Select "Help" → "Check for Updates"
- Install all updates from Freescale/NXP - these are denoted by
com.freescale.xxxorcom.nxp.xxx. There may also be updates for things such as toolchain or debug interfaces. While these additional updates are typically OK to install, sometimes they may cause issues since they aren't released as part of the KDS toolchain

Build an Example Application
The following steps will guide you through opening the hello_world application. These steps may change slightly for other example applications as some of these applications may have additional layers of folders in their path.
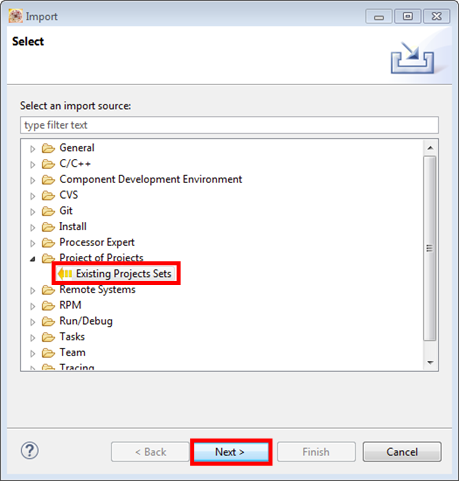
- Select File → Import from the KDS IDE menu. In the window that appears, expand the "Project of Projects" folder and select "Existing Project Sets". Then, click the "Next" button
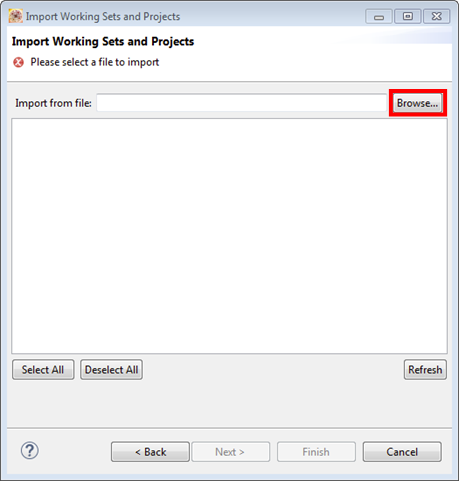
- Click the "Browse" button next to the "Import from file" option
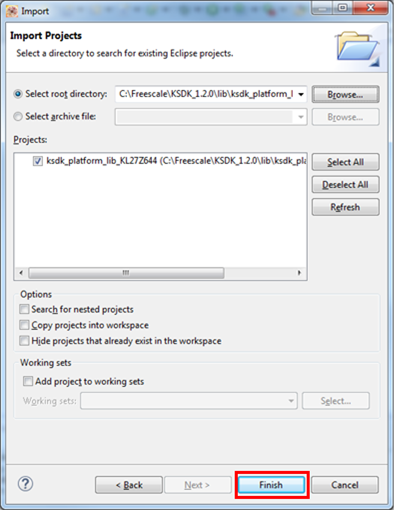
Point to the example application project, which can be found using this path:
<install_dir>/boards/<board_name>/<example_type>/<application_name>/kdsFor this guide, choose the specific location:
<install_dir>/boards/KV10Z32/demo_apps/hello_world/kds- After pointing to the correct directory, your "Import Working Sets and Projects" window should look like the figure below. Click the "Finish" button
- There are two project configurations (build targets) supported for each KSDK project:
- Debug: Compiler optimization is set to low, and debug information is generated for the executable. This target should be selected for development and debug
- Release: Compiler optimization is set to high, and debug information is not generated. This target should be selected for final application deployment
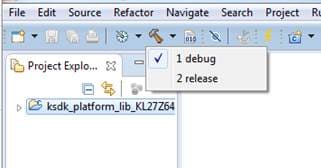
- Choose the appropriate build target, "Debug" or "Release", by clicking the downward facing arrow next to the hammer icon, as shown below. For this example, select the "Debug" target
- The library starts building after the build target is selected. To rebuild the library in the future, click the hammer icon (assuming the same build target is chosen)
Run an Example Application
The FRDM-KV10Z board comes loaded with the PEmicro debug interface from the factory. If you have changed the debug OpenSDA application on your board, visit OpenSDA for information on updating or restoring your board to the factory state.
- Connect the development platform to your PC via USB cable between the "SDAUSB" USB port on the board and the PC USB connector
- Open the terminal application on the PC (such as PuTTY or Tera Term) and connect to the debug COM port you determined earlier. Configure the terminal with these settings:
- 115,200 baud rate
- No parity
- 8 data bits
- 1 stop bit
For Linux OS users only, run the following commands in your terminal. These install "libudev" onto your system, which is required by KDS IDE to launch the debugger
12
user@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install libudev-dev libudev1 user@ubuntu:~$ sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libudev.so /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libudev.so.0- Ensure that the debugger configuration is correct for the target you're attempting to connect to. This refers to the OpenSDA interface of your board. If you're unsure what
your board has, please consult Appendix B of the PDF document.
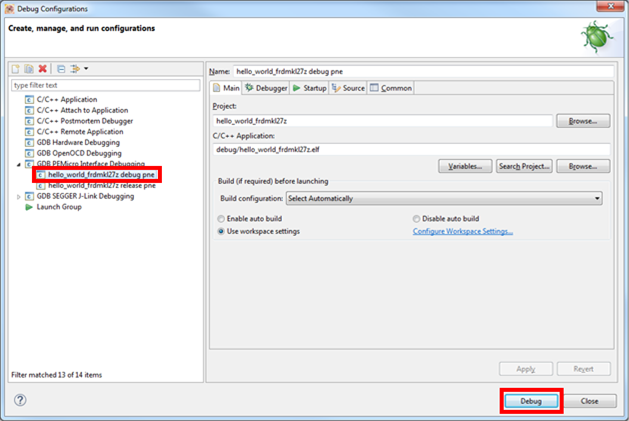
- To check the available debugger configurations, click the small downward arrow next to the green "Debug" button and select "Debug Configurations"

- In the Debug Configurations dialog box, select a debug configuration that corresponds to the hardware platform you're using. For Windows or Linux users, select the GDB PEmicro
option. For Mac users, select J-Link. After selecting the debugger interface, click the "Debug" button to launch the debugger
- To check the available debugger configurations, click the small downward arrow next to the green "Debug" button and select "Debug Configurations"
- The application is downloaded to the target and automatically run to main():

- Start the application by clicking the "Resume" button:

- The
hello_worldapplication is now running and a banner is displayed on the terminal. If this is not the case, check your terminal settings and connections
Using a different toolchain?
Running a demo using IAR
Build a Demo Application
The following steps will guide you through opening the hello_world application. These steps may change slightly for other example applications as some of these applications may have additional layers of folders in their path.
If not already done, open the desired example application workspace. Most example application workspace files can be located using the following path:
<install_dir>/boards/<sdk_board_name>/<example_type>/<application_name>/iarUsing the
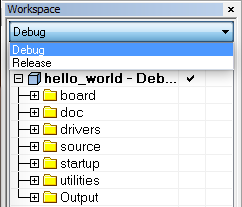
hello_worlddemo as an example, the path is:/boards/frdmkv10z/demo_apps/hello_world/iar - Select the desired build target from the drop-down. For this example, select the "hello_world - Debug" target
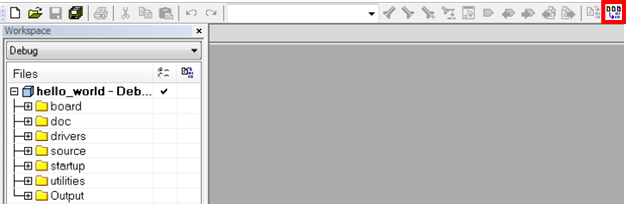
- To build the application, click the "Make" button, highlighted in red below
- The build will complete without errors
Run an Example Application
The FRDM-KV10Z board comes loaded with the PEmicro debug interface from the factory. If you have changed the debug OpenSDA application on your board, visit OpenSDA for information on updating or restoring your board to the factory state.
- Connect the development platform to your PC via USB cable between the "SDAUSB" USB port on the board and the PC USB connector
- Open the terminal application on the PC (such as PuTTY or Tera Term) and connect to the debug COM port you determined earlier. Configure the terminal with these settings:
- 115,200 baud rate
- No parity
- 8 data bits
- 1 stop bit
- Click the "Download and Debug" button to download the application to the target

- The application is then downloaded to the target and automatically runs to the main() function
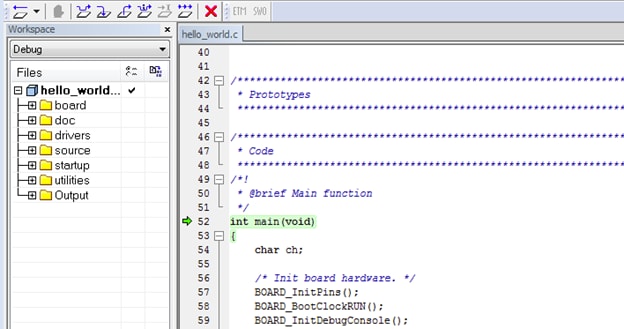
- Run the code by clicking the "Go" button to start the application

- The
hello_worldapplication is now running and a banner is displayed on the terminal. If this is not the case, check your terminal settings and connections
Running a demo using Keil® MDK/µVision®
Install CMSIS device pack
After the MDK tools are installed, Cortex® Microcontroller Software Interface Standard (CMSIS) device packs must be installed to fully support the device from a debug perspective. These packs include things such as memory map information, register definitions and flash programming algorithms. Follow these steps to install the appropriate CMSIS pack.
- Open the MDK IDE, which is called µVision. In the IDE, select the "Pack Installer" icon

- In the Pack Installer window, navigate to the section with the Kinetis packs (they are in alphabetical order). The Kinetis packs start with "Keil::Kinetis" and are followed by the
MCU family name, for example "Keil::Kinetis_KLxx_DFP". Because this example uses the FRDM-KV10Z platform, the KVxx family pack is selected. Click on the "Install" button next to
the pack. This process requires an internet connection to successfully complete
- After the installation finishes, close the Pack Installer window and return to the µVision IDE
Build an Example Application
The following steps will guide you through opening the hello_world application. These steps may change slightly for other example applications as some of these applications may have
additional layers of folders in their path.
If not already done, open the desired demo application workspace in:
<install_dir>/boards/<sdk_board_name>/<example_type>/<application_name>/mdkThe workspace file is named <application_name>.uvmpw, so for this specific example, the actual path is:
<install_dir>/boards/frdmkv10z/demo_apps/hello_world/iar/hello_world.uvmpw- To build the demo project, select the "Rebuild" button, highlighted in red

- The build will complete without errors
Run an Example Application
The FRDM-KV10Z board comes loaded with the PEmicro debug interface from the factory. If you have changed the debug OpenSDA application on your board, visit OpenSDA for information on updating or restoring your board to the factory state.
- Connect the development platform to your PC via USB cable between the "SDAUSB" USB port on the board and the PC USB connector
- Open the terminal application on the PC (such as PuTTY or Tera Term) and connect to the debug COM port you determined earlier. Configure the terminal with these settings:
- 115,200 baud rate
- No parity
- 8 data bits
- 1 stop bit
- After the application is properly built, click the "Download" button to download the application to the target
- After clicking the "Download" button, the application downloads to the target and should be running. To debug the application, click the "Start/Stop Debug Session" button,
highlighted in red

- Run the code by clicking the "Run" button to start the application

- The
hello_worldapplication is now running and a banner is displayed on the terminal. If this is not the case, check your terminal settings and connections
Running a demo using Arm® GCC
Set Up Toolchain
This section contains the steps to install the necessary components required to build and run a KSDK demo application with the Arm GCC Toolchain, as supported by the Kinetis SDK.
There are many ways to use Arm GCC tools, but this example focuses on a Windows environment. Though not discussed here, GCC tools can also be used with both Linux OS and Mac OSX.
Install GCC Arm Embedded Toolchain
Download and run the installer from GNU Arm Embedded Toolchain . This is the actual toolchain (i.e., compiler, linker, etc.). The GCC toolchain should correspond to the latest supported version, as described in the Kinetis SDK Release Notes.
Install MinGW
The Minimalist GNU for Windows (MinGW) development tools provide a set of tools that are not dependent on third party C-Runtime DLLs (such as Cygwin). The build environment used by the KSDK does not utilize the MinGW build tools, but does leverage the base install of both MinGW and MSYS. MSYS provides a basic shell with a Unix-like interface and tools.
- Download the latest MinGW
mingw-get-setupinstaller from MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows Files - Run the installer. The recommended installation path is
C:\MinGW, however, you may install to any location - Ensure that the "mingw32-base" and "msys-base" are selected under Basic Setup

- Click "Apply Changes" in the "Installation" menu and follow the remaining instructions to complete the installation

Add the appropriate item to the Windows operating system Path environment variable. It can be found under "Control Panel → System and Security → System → Advanced System Settings" in the "Environment Variables..." section. The path is:
<mingw_install_dir>\binAssuming the default installation path,
C:\MinGW, an example is shown below. If the path is not set correctly, the toolchain will not work
Add a New Environment Variable for ARMGCC_DIR
-
Create a new system environment variable and name it ARMGCC_DIR. The value of this variable should point to the Arm GCC Embedded Toolchain installation path, which, for this example, is:
C:\Program Files (x86)\GNU Tools Arm Embedded\4.9 2015q3Reference the installation folder of the GNU Arm GCC Embedded tools for the exact path name of your installation

Install CMake
- Download CMake 3.0.x from CMake
- Install CMake, ensuring that the option "Add CMake to system PATH" is selected when installing. It's up to the user to select whether it's installed into the PATH for all users
or just the current user. In this example, the assumption is that it's installed for all users

- Follow the remaining instructions of the installer
- You may need to reboot your system for the PATH changes to take effect
Build an Example Application
To build an example application, follow these steps.
- If not already running, open a GCC Arm Embedded Toolchain command window. To launch the window, from the Windows operating system Start menu, go to "Programs → GNU Tools Arm
Embedded <version>" and select "GCC Command Prompt"
Change the directory to the example application project directory, which has a path like this:
<install_dir>/boards/<board_name>/<example_type>/<application_name>/armgccFor this guide, the exact path is:
<install_dir>/boards/frdmkv10z/demo_apps/hello_world/armgcc- Type "build_debug.bat" on the command line or double click on the "build_debug.bat" file in Windows operating system Explorer to perform the build. The output is shown in this
figure:
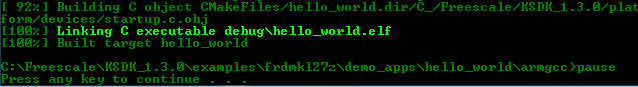
Run an Example Application
The GCC tools require a J-Link debug interface. To update the OpenSDA firmware on your board to the latest J-Link app, visit OpenSDA. After installing the J-Link OpenSDA application, download the J-Link driver and software package from SEGGER Downloads .
- Connect the development platform to your PC via USB cable between the "SDAUSB" USB port on the board and the PC USB connector
- Open the terminal application on the PC (such as PuTTY or Tera Term) and connect to the debug COM port you determined earlier. Configure the terminal with these settings:
- 115,200 baud rate
- No parity
- 8 data bits
- 1 stop bit
- Open the J-Link GDB Server application. Assuming the J-Link software is installed, the application can be launched by going to the Windows operating system Start menu and selecting "Programs → SEGGER → J-Link <version> J-Link GDB Server"
- Modify the settings as shown below. The target device selection chosen for this example is the "MKV10Z32xxx7"

- After it is connected, the screen should resemble this figure:
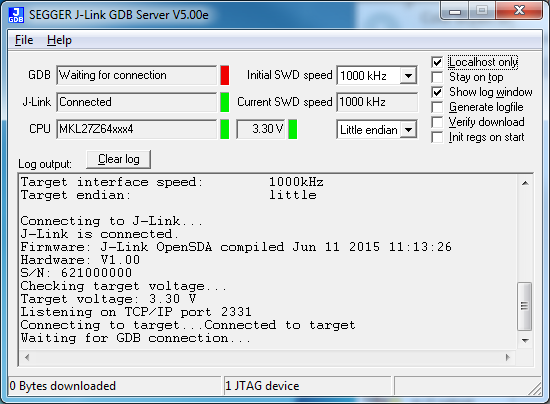
- If not already running, open a GCC Arm Embedded Toolchain command window. To launch the window, from the Windows operating system Start menu, go to "Programs → GNU Tools Arm
Embedded
<version>" and select "GCC Command Prompt"

Change to the directory that contains the example application output. The output can be found in using one of these paths, depending on the build target selected:
<install_dir>/<example_type>/<application_name>/armgcc/debug<install_dir>/<example_type>/<application_name>/armgcc/releaseFor this guide, the path is:
<install_dir>/boards/frdmkv10z/demo_apps/hello_world/armgcc/debug- Run the command "arm-none-eabi-gdb.exe
<demo_name>.elf". For this example, it is "arm-none-eabi-gdb.exe hello_world.elf"
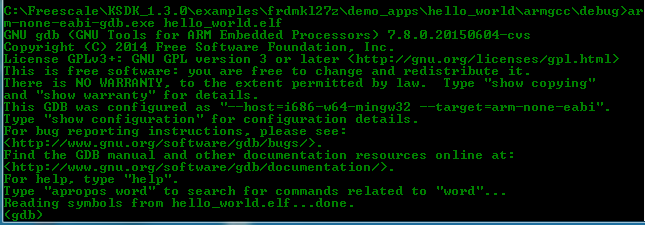
- Run these commands:
- target remote localhost:2331
- monitor reset
- monitor halt
- load
- monitor reset
- The application is now downloaded and halted at the reset vector. Execute the "monitor go" command to start the example application
- The
hello_worldapplication is now running and a banner is displayed in the terminal window