Software enablement of sensors is a must-have feature for implementation of
IoT applications. Two weeks ago, the NXP released Version 1.0 of the ISSDK
(IoT Sensing Software Development Kit) into the Kinetis Software Development
Kit (KSDK) ecosystem. Depending upon your MCU, when you use the
Kinetis Expert (KEx) System Configuration Tool to generate a version of the KSDK, you will have the option to include
drivers and sample applications for a variety of NXP sensor
components. ISSDK provides a much simpler interface than the
Intelligent Sensing Framework (ISF)
historically offered by Freescale and now NXP. Drivers are included for
the following sensors:
| Sensor Part Number |
Sensor Type |
Interface |
| FXAS21002C |
Gyroscope |
SPI and I2C |
| FXLC95000CL |
Intelligent Accelerometer |
SPI and I2C |
| FXLS8471Q |
Digital Accelerometer |
SPI and I2C |
| FXOS8700C |
Digital Accelerometer and Magnetometer |
SPI and I2C |
| MAG3110 |
Digital Magnetometer |
I2C |
MMA8451Q
MMA8452Q
MMA8453Q
|
Digital Accelerometer |
I2C |
| MMA8491Q |
Digital Accelerometer |
I2C |
MMA8652FC
MMA8653FC
|
Digital Accelerometer |
I2C |
| MMA9553L |
Intelligent Accelerometer |
I2C and SPI |
| MPL3115A2 |
Digital Pressure |
I2C |
Supported board combinations include:
Sample applications are included for sensor shields as a function of the
sensors on each shield. NXP Sensor Fusion for Kinetis MCUs Version 7.00
examples are provided for the 1st three rows in the table above.
Supported development environments include:
-
Kinetis Design Studio IDE v3.2
- IAR Embedded Workbench for Arm version 7.50.1
- MDK-ARM Microcontroller Development Kit (Keil)® 5.17
-
Makefiles support with GCC revision 4.9-2015-q3-update from Arm Embedded
- Atollic® TrueSTUDIO® 5.4.0
Pedometer examples are only supported for IAR.
Getting ISSDK is easy. Navigate to https://mcuxpresso.nxp.com/en/welcome.
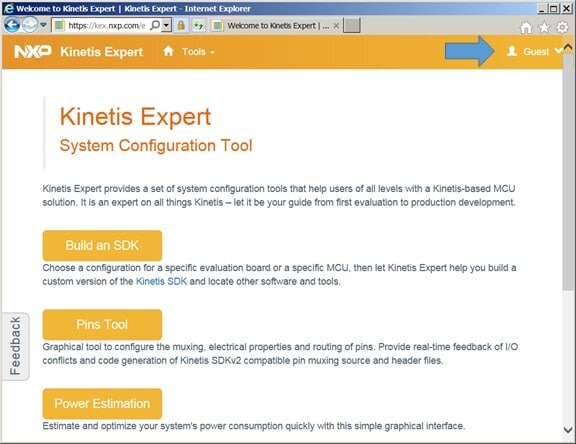
Navigate to https://mcuxpresso.nxp.com/en/welcome
Login in using the link in the upper right. Once logged in, select the
“Build and SDK” button.
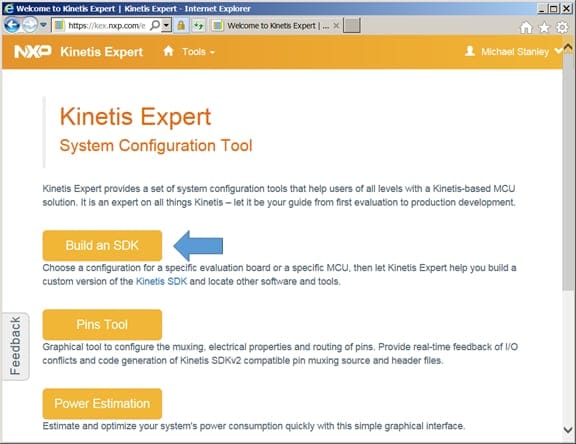
Select “Build an SDK”
You can get portions of ISSDK via either “Boards” or
“Kits” in the next dialog. I suggest you select
“Boards” as it will give you content for all supported sensor
shields in one step.
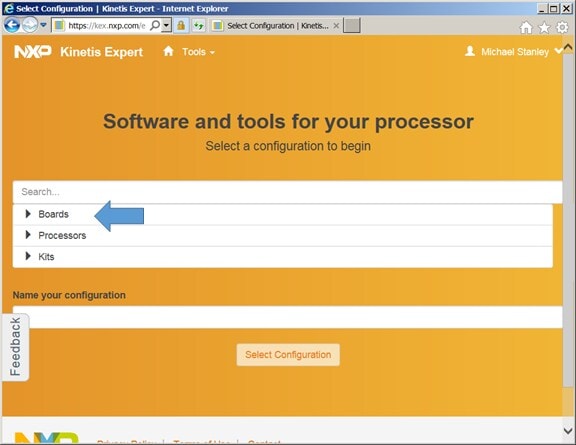
Select “Boards”
Choose your base board from the list that appears. Remember, ISSDK
is not supported for all boards, only those in the list above.

Select your base board
Now it’s time to specify your configuration. I recommend you:
- Check the ISSDK checkbox (otherwise, why are you reading this?)
- Check FreeRTOS (used for Sensor Fusion projects)
- Select “All Toolchains”
- and only then click “Build SDK Package”
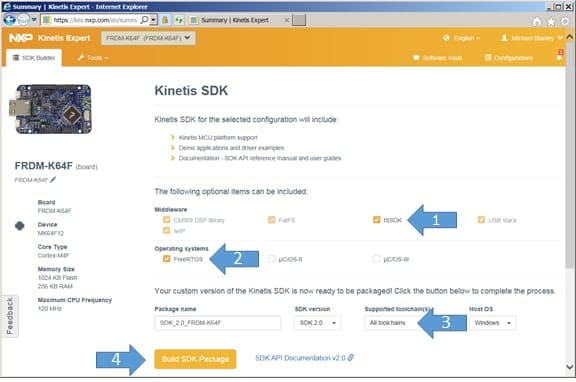
Configure options shown above
You will eventually get an email notification that your KSDK kit file is
available for download. Navigate to the software vault, update all
information in your preferences to enable the download icon if it is not
visible/active, and finally click the download icon for your kit.

Time to download your KSDK
You will be prompted to accept the license terms.

Accept License Terms
Then download to your location of choice and unzip the downloaded file.

Specify where you want to install your KSDK
At this point, you should have the full ISSDK installation.
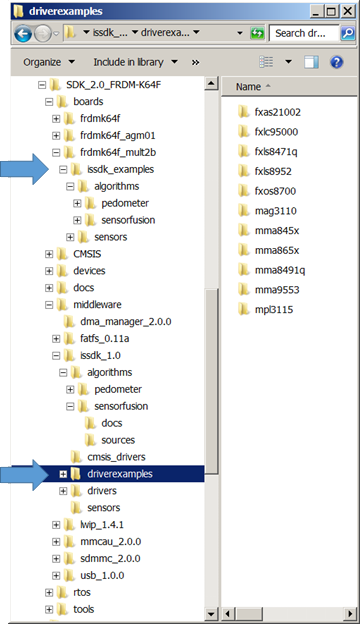
The resulting directory structure
The figure above shows FRDM-K64F KSDK structure. You might start by
exploring the two folders indicated, as they contain full sample
programs. Each example in the driverexamples folder shows you how to
interface with just one device. You’ll find fuller application in
the boards/issdk_examples directory.
In the event you did not create the configuration you wanted, simply delete
the folder you created with the unzip step, return to https://mcuxpresso.nxp.com/en/welcome, delete the
old vault and configuration entries and start over. Since I commonly
switch between boards, I keep several KSDK variants installed under a common
folder on my hard drive.
I will dive into details of the included Sensor Fusion Version 7.00 in future
postings. In the meantime, enjoy!
Michael Stanley “works” on fun sensors and systems
topics.













