The smart thermostat market is projected to grow to over 5.9 billion by 2020
across various applications including residential, commercial and industrial.
To keep up with this growth, startups and established companies need a way to
streamline their design process and find an inexpensive, versatile and easy to
use development solution to take a proof of concept into production as quickly
as possible. By saving time developing a prototype, developers can spend more
time incorporating key differentiating factors into designs that maximize
revenue.
Solution
To accelerate the design of IoT devices, NXP has introduced the
Rapid IoT prototyping kit. It integrates eleven NXP devices (microcontroller, low-power connectivity,
sensors, NFC, secure element, power management, interface) in a small
form-factor hardware design and combines it with proven software enablement
(drivers, RTOS, middleware, cloud connect) and a web IDE with GUI-based
programming. Refer to Figure 1 for the complete block diagram.
Rapid IoT provides the easiest path for anyone to take their connected device
to a proof-of-concept by simplifying the design process. It eliminates the
need to write code and integrates all the necessary functions required by an
IoT device including the ability to sense, think and act.
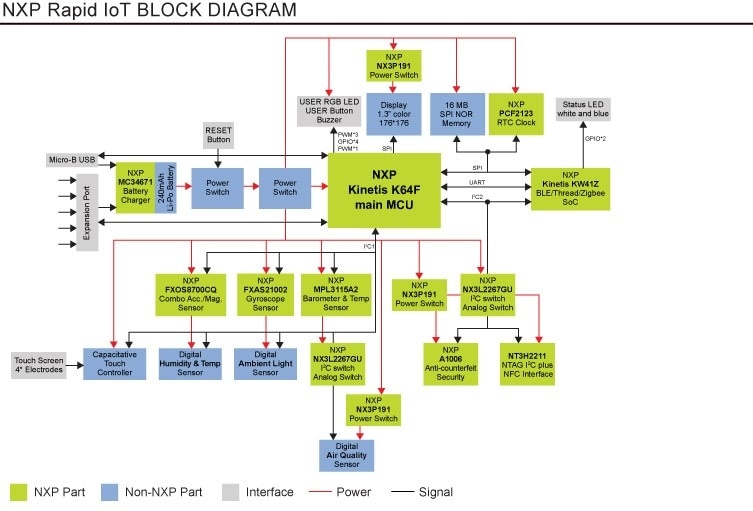
Figure 1. Rapid IoT Prototyping Kit Block Diagram
Design Considerations and Implementation
Consider the image shown in Figure 2. The picture to the right is a
traditional AC system and control unit and the picture to the left is the
smart thermostat control design using the Rapid IoT kit. The traditional
system includes a wall mounted indoor unit and a control unit to control the
room temperature. These systems are bulky and expensive and do not include
software, user-friendly interfaces, online connectivity and access to cloud
storage for data analysis. In contrast, a smart thermostat control design
incorporates all of the above and results in a cost-effective, efficient and
easy to control solution.
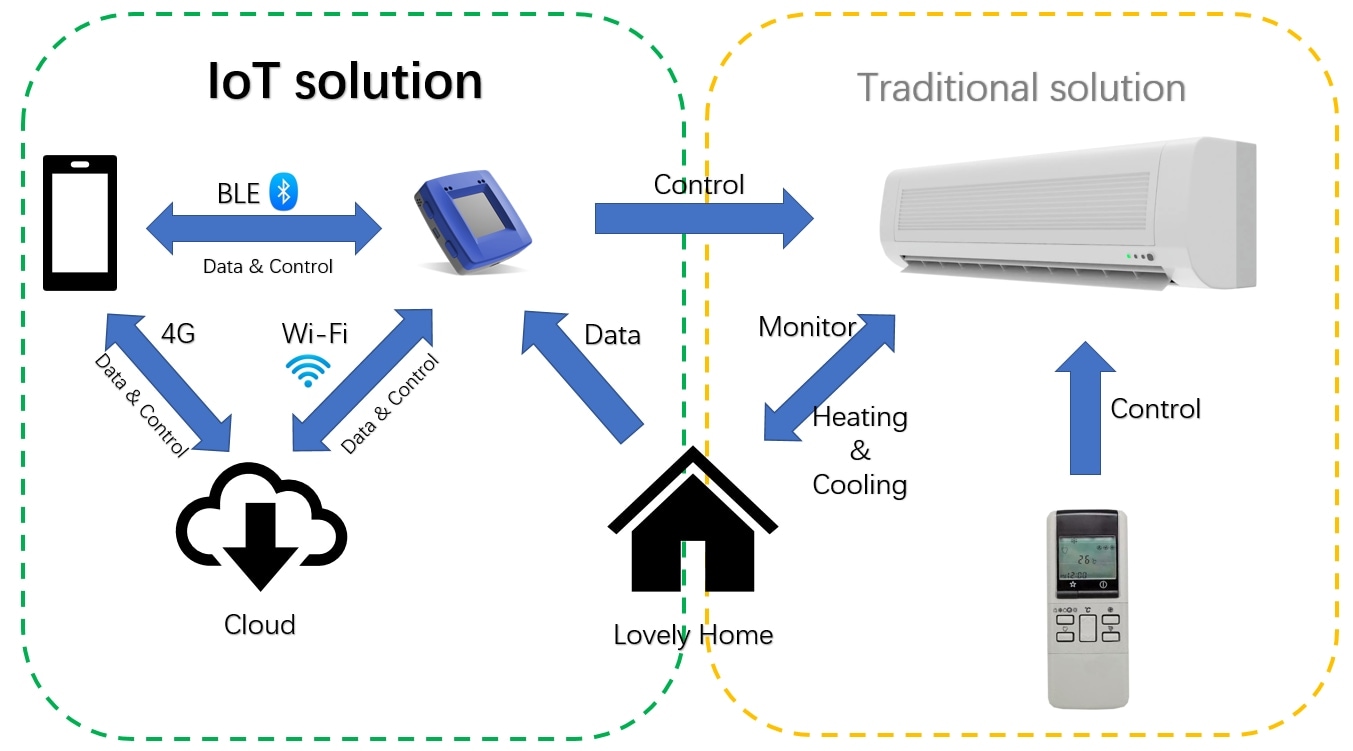
Figure 2. Smart Thermostat Control Design w/ Rapid IoT vs Traditional AC
system Control Design
To design a smart thermostat control using the Rapid IoT kit, the following
criteria was considered:
-
The control unit should have a UI to locally manage and control the
thermostat.
-
The smart device should have a UI to wirelessly manage and control the
thermostat via Bluetooth Low Energy or Wi-Fi.
-
Data processed and acquired can be uploaded securely to the cloud for future
analysis.
Results
To achieve this, the Rapid IoT design incorporates a temperature, humidity and
air quality sensor. These parameters can be locally or remotely controlled by
the Rapid IoT hardware or a smartphone, respectively. Wireless connectivity is
possible via Bluetooth Low Energy or Wi-Fi while the hardware and smartphone
UI was easily designed using the Rapid IoT Studio IDE tool without writing a
single line of code and instead, using a drag and drop style of programming.
To secure data uploads to the cloud, a secure tamper resistant authentication
device is used.
Figures 3 and 4 show the Rapid IoT studio environment and the smart thermostat
control function design and hardware. Figures 5 shows the Rapid IoT smartphone
UI design and Figure 6 shows the smartphone application, which can be used to
wirelessly monitor and control the control unit.
All the necessary files to build and test this design can be found
in this NXP community thread.
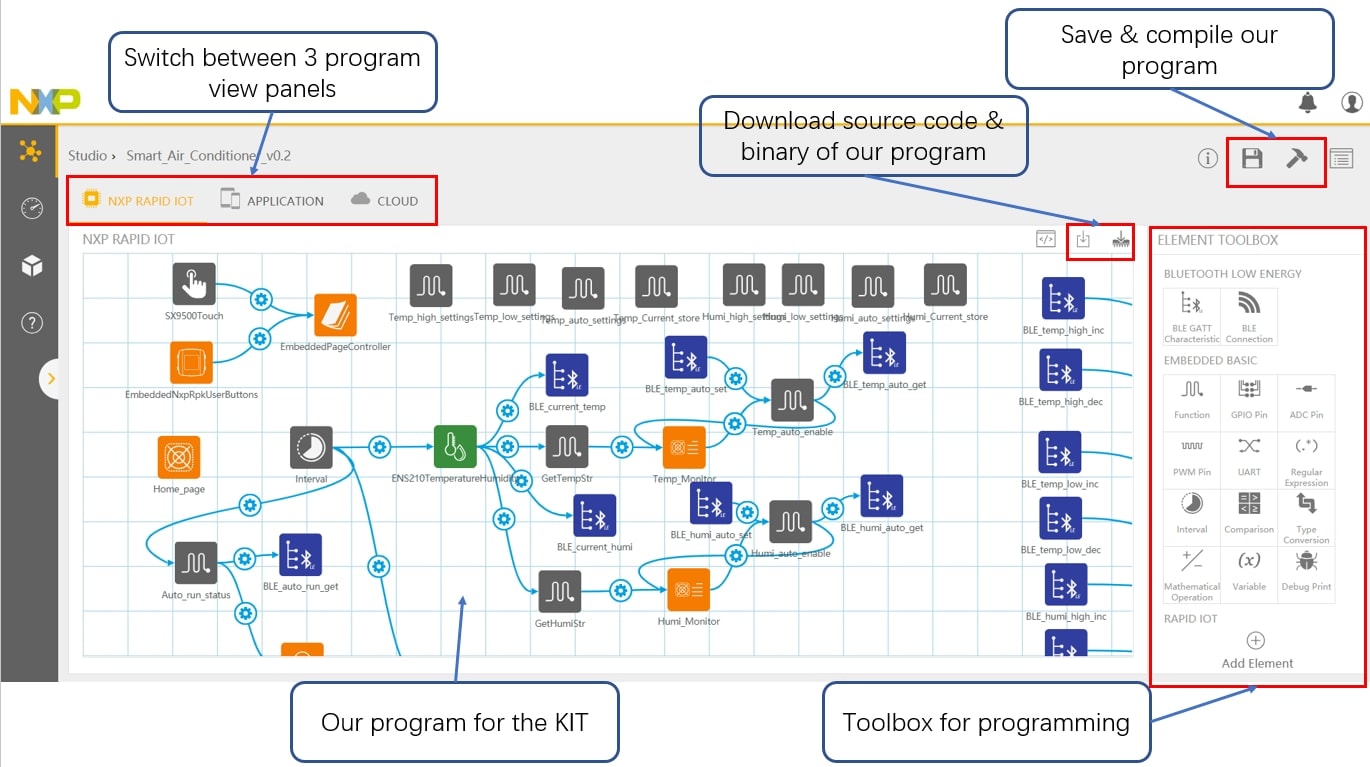
Figure 3. Rapid IoT Studio – Function Design

Figure 4. Rapid IoT Kit Hardware – Control Unit UI
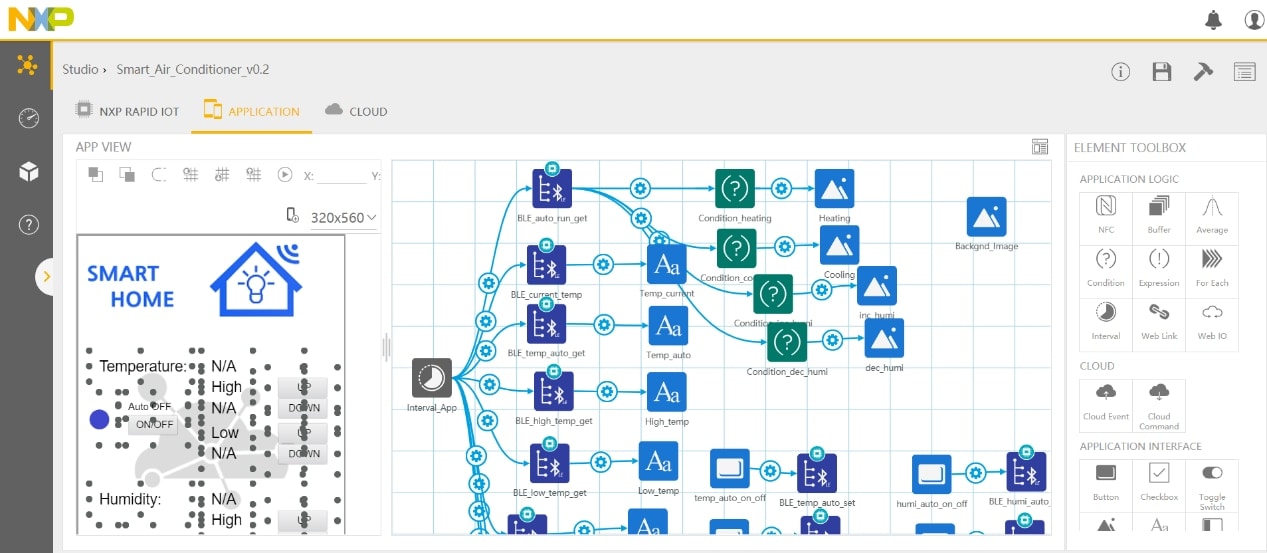
Figure 5. Rapid IoT Studio –Smart Phone UI Design
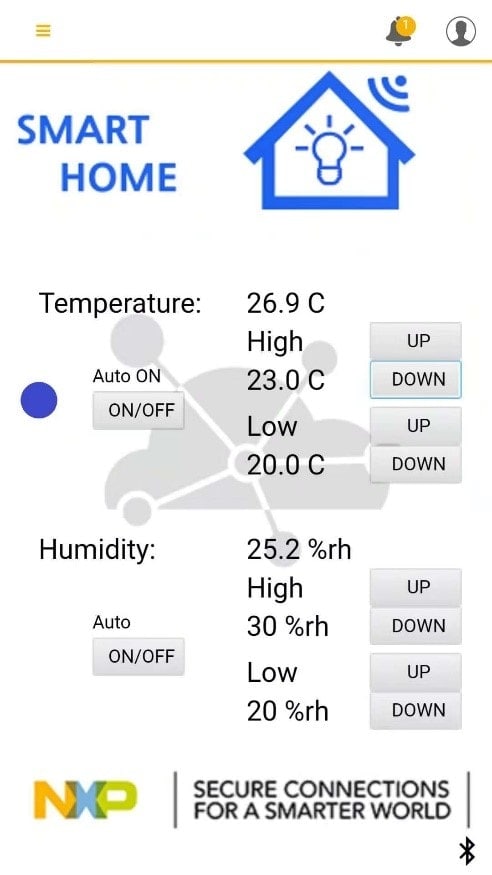
Figure 6. Smart Phone Application UI for Wireless Management and Control
Additional Resources
Get Rapid IoT Prototyping Kit Today
Step-by-Step Easy to Follow Setup Instructions
Sources:
Market data
Smart Thermostat Market
Category/keywords:
Rapid prototyping, Rapid iot, iot design, smart thermostat, smart thermostat
control unit, online ide, development board, iot kit, prototyping, thermostat
solution, rapid prototyping software, rapid app, rapid prototyping software
development, Internet of things starter kit.
Authors












